Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect bones and keep your joints stable. When they get stretched or torn, especially around the knee, it can be painful and limit movement. Thankfully, with the right care especially Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment you can recover fully and safely.
Have you ever twisted your knee while playing sports or just walking on uneven ground? I did, and the pain was sharp and scary. I couldn’t walk properly, and my knee felt weak for weeks. After seeing a physiotherapist, I learned about Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment and it completely changed my recovery.
Understanding Knee Ligament Injuries
The knee has four main ligaments:
- ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament)
- PCL (Posterior Cruciate Ligament)
- MCL (Medial Collateral Ligament)
- LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament)
These ligaments keep your knee steady when you move. If you twist your leg too far or land the wrong way, one of these can tear or stretch. This is where Physiotherapy Treatment for Knee Ligament Injury becomes important. It helps rebuild strength and flexibility after the injury.
Role of Physiotherapy Treatment for Knee Ligament Injury Recovery
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the recovery of knee ligament injuries. Here are some key ways in which physiotherapy benefits patients:
- Pain Management: Physiotherapists use various techniques to reduce pain and inflammation in the injured knee.
- Restoring Range of Motion: Exercises and stretches help improve flexibility and range of motion in the knee joint.
- Strengthening Muscles: Physiotherapy treatment for knee ligament injury focuses on strengthening the muscles around the knee, providing better support to the injured ligaments. This approach helps stabilize the joint, reduce stress on the affected ligaments, and enhance overall knee stability. Physiotherapists tailor exercises to target specific muscle groups, gradually building strength and function, which is instrumental in the rehabilitation process for knee ligament injuries.
- Balance and Coordination: Physiotherapy helps improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of re-injury.
- Functional Training: Patients learn how to perform daily activities with the least amount of strain on the knee.
How Physical Therapy Helps Heal Ligaments?
So, what is the best treatment for knee ligament damage? In many cases, it’s not surgery — it’s physiotherapy.
Here’s how it helps:
- Reduces pain and swelling
- Strengthens muscles around the knee
- Improves balance and flexibility
- Prevents re-injury
- Gets you back to your normal activities safely
Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment is not just about healing. It’s about building your body back stronger and smarter.

Stages of Physiotherapy Treatment
Effective physiotherapy treatment for knee ligament injuries typically progresses through several stages:
- Initial Assessment: A physiotherapist evaluates the extent of the injury, assesses the patient’s range of motion, and develops an individualized treatment plan.
- Pain and Inflammation Management: Techniques such as ice therapy and ultrasound are used to reduce pain and swelling.
- Range of Motion and Strengthening: Exercises target improving knee flexibility and muscle strength.
- Functional Training: Patients learn how to perform specific movements that mimic daily activities while protecting the injured knee.
- Sport-Specific Training (if applicable): Athletes may undergo specialized training to prepare for a return to sports activities.
Physiotherapy treatment for knee ligament injury provides a non-invasive recovery option, often effective for less severe cases when surgery is not the first choice.
- Assessment and Diagnosis: In knee ligament treatment without surgery, the process starts with a comprehensive assessment by a physiotherapist to gauge the extent of the injury, guiding the appropriate physiotherapy plan.
- Pain Management: Physiotherapy focuses on reducing pain and swelling, often through modalities such as ice, heat, or ultrasound therapy. This helps patients feel more comfortable during the recovery process.
- Strengthening Exercises: Physiotherapists design customized exercise programs to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint. Strong muscles can help stabilize the joint and provide better support to the injured ligament.
- Range of Motion: Restoring the full range of motion in the knee joint is a crucial goal. Physiotherapy uses various techniques, including stretching and mobility exercises, to regain flexibility.
- Functional Rehabilitation: In physiotherapy treatment for knee ligament injury, physiotherapists frequently employ a tailored approach by simulating functional movements and activities that are integral to the patient’s daily life or sports, with the aim of helping them regain their pre-injury abilities.
- Patient Education: Patients are educated on proper body mechanics, posture, and exercises that they can continue at home to maintain progress between therapy sessions.
- Progress Monitoring: The physiotherapist continuously monitors the patient’s progress and adjusts the treatment plan as needed.
- Preventing Recurrence: In knee ligament treatment without surgery, physiotherapy emphasizes patient education on strategies to prevent re-injury and establish a solid foundation for long-term knee health.
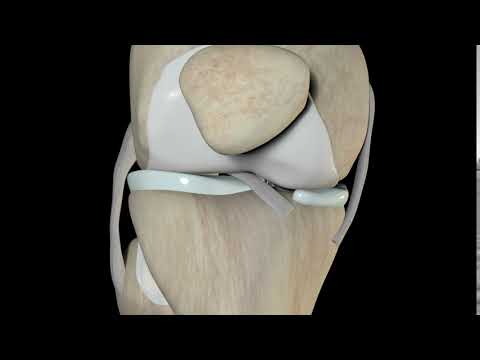
Causes of Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee ligament injuries can happen to anyone. Common causes include:
- Sports like football, basketball, or skiing
- Sudden stops or changes in direction
- Accidents or falls
- Weak muscles or poor balance
Once injured, rest alone might not be enough. That’s why many doctors recommend Physiotherapy Treatment for Knee Ligament Injury as part of the recovery plan.
Symptoms of Knee Ligament Injuries
How do you know if you’ve hurt a ligament? Here are the most common signs:
- Sudden pain after twisting or falling
- Swelling around the knee
- Difficulty walking or standing
- A “pop” sound at the time of injury
- Feeling like the knee will “give out”
If you feel these symptoms, you might need Physiotherapy for ligament tear of knee to recover properly.
How Serious Is a Knee Ligament Tear?
Knee ligament tears can be mild, moderate, or severe. Here’s what that means:
- Grade 1 (Mild): Slight stretch, no major damage
- Grade 2 (Moderate): Partial tear
- Grade 3 (Severe): Complete tear
A mild tear might heal in a few weeks with Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment, while a complete tear could take months and may require surgery. Either way, physiotherapy is usually needed for a full recovery.
When to See a Doctor or Therapist:
- Pain lasts more than a few days
- You can’t bend or straighten your knee
- The knee feels unstable or wobbly
Remember, what is the best treatment for knee ligament damage? Often, it starts with early and proper physiotherapy.
Key Exercises for Strengthening Injured Ligaments
During Physiotherapy for ligament tear of knee, your therapist will guide you through different exercises. These help you move better and protect your knee.
Some key exercises include:
- Quad Sets – Tighten your thigh muscles while lying down.
- Heel Slides – Slide your heel back to bend your knee slowly.
- Straight Leg Raises – Lift your leg without bending the knee.
- Bridges – Strengthen glutes and hamstrings.
- Step-Ups – Practice controlled steps to improve stability.
These moves may look simple, but they are powerful when done correctly under a therapist’s care. It’s one of the reasons why Physiotherapy Treatment for Knee Ligament Injury works so well.
Conclusion
Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment is a non-invasive, effective, and often essential path to recovery. With the guidance of skilled physiotherapists, patients can regain strength, flexibility, and function in their knees, helping them return to their daily activities, sports, and an improved quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with an ACL, MCL, or PCL injury, Ligament Injury Physiotherapy Treatment offers a tailored approach to rehabilitation. It typically involves pain management, personalized exercise programs, range of motion exercises, balance training, and patient education.
