Joint replacement surgery involves replacing a damaged or worn-out joint with an artificial implant. It’s commonly performed on hips, knees, and shoulders to relieve pain and improve function in patients with severe arthritis, trauma, or other joint disorders. The procedure typically involves removing the damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with metal, plastic, or ceramic components designed to mimic natural joint movement. Recovery includes physical therapy to restore strength and mobility. Joint replacement surgery can significantly enhance quality of life by reducing pain and improving joint function, allowing patients to return to their daily activities with greater ease.
What is joint replacement surgery?
Joint replacement surgery is a medical procedure where a damaged or arthritic joint is removed and replaced with a prosthesis made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials. This surgery is most commonly performed on the hip, knee, and shoulder joints to alleviate pain and restore function when conservative treatments fail. The procedure involves removing the damaged joint surfaces and implanting new, artificial components designed to replicate the natural movement of the joint. Post-surgery, patients typically undergo physical therapy to regain strength and mobility. Joint replacement surgery can significantly improve quality of life by reducing pain and enhancing joint functionality.
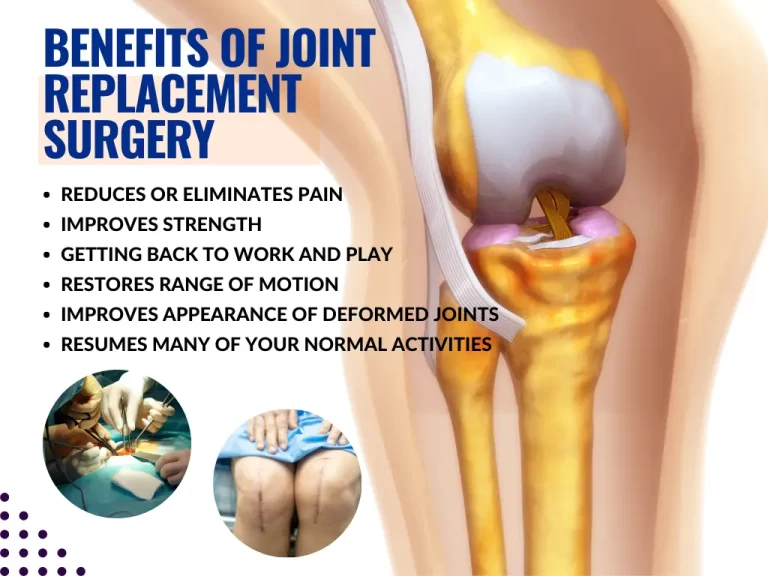
Benefits of Joint Replacement Surgery
- Pain Relief: One of the primary benefits is the significant reduction or complete elimination of joint pain, allowing patients to return to their daily activities with minimal discomfort.
- Improved Mobility: The surgery restores joint function, leading to better mobility and the ability to perform everyday tasks more easily.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By reducing pain and improving movement, joint replacement surgery can greatly enhance a patient’s overall quality of life, allowing for more active and independent living.
- Increased Activity Levels: Patients often experience increased activity levels post-surgery, enabling them to participate in physical activities and exercises that were previously too painful or difficult.
- Long-Term Solution: Joint replacements can last many years, providing a long-term solution to chronic joint issues and improving long-term joint health.
- Correction of Deformities: The surgery can correct joint deformities and improve the alignment of the affected joint, leading to better function and aesthetics.
- Reduction in Use of Medications: Successful joint replacement can reduce or eliminate the need for pain medications, which can have side effects and long-term health implications.
- Psychological Benefits: Improved physical function and pain relief can lead to better mental health, reducing anxiety and depression associated with chronic joint pain.
Joint Reconstruction Vs Joint Replacement
Joint Reconstruction is a surgical procedure that is done to repair and restore the function in a joint while joint replacement surgery involves in removing a damaged joint completely and replacing it with a new one.
Typically, joint reconstruction is preferrable unless a joint is damaged beyond repair, and when joint replacement is necessary. Joint reconstruction surgery might be necessary if your doctor suggests you to undergo any of the following procedures:
- Deformity correction.
- Cartilage transplant.
- Patella realignment.
- Knee multi-ligament reconstruction.
- Joint resurfacing.
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries.
With joint reconstruction surgery, the relief provided is only temporary but the recovery is shorter and easier and with a total joint replacement surgery in Chennai, the relief is long-lasting and recovery also takes more time.
Basic Treatment of Joint Reconstruction Surgery
The first step to recover from any joint injury is the RICE method – Rice, Ice, Compression and Elevation. You should start using braces with joint movement especially if it’s a sports injury. At the same time, it is essential to maintain your weight and manage muscle tone for a healthy body and rapid recovery. If your muscles atrophy, it can cause more pressure on joints so it is vital to do a physical therapy to speed up the recovery.
It is always best to start with minimally invasive treatments before opting for joint replacement surgery in Chennai. However, in some cases such as arthritis, dislocations, bursitis, serious injury or muscle tears, surgery may be required.
If you have tried all the basic treatments and still dealing with lack of movement or pain, then you should consult with your doctor about a joint replacement or joint reconstruction surgery. Each of these procedures has slightly different ramifications.
Types of Join Replacement
Joint replacement surgery comes in several types, primarily focused on different joints and the extent of replacement required. The most common types are:
- Total Joint Replacement: Involves replacing the entire damaged joint with a prosthesis, commonly performed on hips, knees, and shoulders.
- Partial Joint Replacement: Only the damaged part of the joint is replaced, often used in knee surgeries where only one compartment of the knee is affected.
- Revision Joint Replacement: A second surgery to replace a worn-out or failed joint replacement with a new one.
- Minimally Invasive Joint Replacement: Utilizes smaller incisions and advanced techniques for quicker recovery and less postoperative pain.
What is Arthroplasty?
The meaning of arthroplasty is surgical joint replacement. During the method, your medical services supplier eliminates a harmed joint and replaces it with a counterfeit joint. The fake joint (prosthesis) can be metal, artistic, or rock-solid plastic. The new joint seems to be the normal joint and moves likewise. Specialists can supplant joints in any piece of your body, yet the most widely recognized kinds of arthroplasty are hip replacement and knee replacement.
Preparing for Joint Replacement Surgery
- Medical Evaluation: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of medical history, to ensure you are healthy enough for surgery.
- Physical Therapy: Start pre-surgery physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the joint, which can aid in recovery.
- Medication Review: Discuss current medications with your doctor. You may need to stop certain medications, such as blood thinners, before surgery.
- Home Preparation: Arrange your home for post-surgery recovery, including moving items for easy access, setting up a recovery area, and arranging for help with daily activities.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stop smoking and limit alcohol consumption to reduce surgery and recovery risks.
- Weight Management: Achieve a healthy weight to minimize pressure on the new joint and improve surgical outcomes.
- Infection Prevention: Follow guidelines for pre-surgery hygiene, including any recommended antibacterial washes, to reduce infection risk.
- Fasting: Follow instructions regarding fasting before surgery to ensure a safe procedure.
- Hospital Bag: Pack a bag with essentials such as comfortable clothing, toiletries, medications, and any necessary medical documents.
Procedures Followed in Different Types of Joint Replacement Surgeries
- Total hip replacement.
- Revision hip replacement.
- Knee joint replacement.
- Shoulder joint replacement.
- Hip joint replacement.
Total Hip Replacement
- Preoperative Assessment: Comprehensive medical evaluation and imaging studies.
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: An incision is made over the hip joint.
- Removal of Damaged Joint: The femoral head is removed, and the acetabulum is cleaned.
- Implant Placement: A metal stem is placed into the femur, and a metal or ceramic ball is attached. A cup is placed in the acetabulum.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy begins shortly after surgery.
Revision Hip Replacement
- Preoperative Assessment: Detailed evaluation and imaging to assess the condition of the current implant.
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: Made over the hip, often using the previous scar.
- Removal of Old Implant: The old prosthesis is carefully removed.
- Implant Placement: A new prosthesis is implanted.
- Closure: The incision is closed.
- Rehabilitation: Intensive physical therapy is initiated.
Knee Joint Replacement
- Preoperative Assessment: Medical evaluation and knee imaging.
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: Made over the knee.
- Removal of Damaged Joint: Damaged cartilage and bone are removed.
- Implant Placement: Metal and plastic components are fitted into the femur, tibia, and patella.
- Closure: The incision is closed.
- Rehabilitation: Early mobilization and physical therapy are critical.
Shoulder Joint Replacement
- Preoperative Assessment: Medical evaluation and shoulder imaging.
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: An incision is made over the shoulder joint.
- Removal of Damaged Joint: Damaged portions of the humeral head and glenoid are removed.
- Implant Placement: A metal ball is attached to the humerus and a plastic socket to the glenoid.
- Closure: The incision is closed.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to restore shoulder function.
Hip Joint Replacement
- Preoperative Assessment: Comprehensive medical evaluation and hip imaging.
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Incision: An incision is made over the hip.
- Removal of Damaged Joint: The damaged hip joint components are removed.
- Implant Placement: The hip socket is replaced with a prosthetic cup, and a metal stem is placed in the femur with a prosthetic ball on top.
- Closure: The incision is closed.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy begins soon after surgery to regain mobility and strength.
Risks of Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery, while generally safe and successful, carries some inherent risks. These include:
- Infection: Surgical site infections can occur and may necessitate further treatment.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism are potential complications.
- Implant Issues: Joint implants may wear out or loosen over time, requiring revision surgery.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: In rare cases, nearby structures can be affected during surgery.
- Pain and Swelling: Some patients experience persistent pain and swelling post-surgery.
- Anesthesia Risks: Adverse reactions to anesthesia are possible.
Patients should thoroughly discuss potential risks with their healthcare team before undergoing joint replacement surgery.
Joint Replacement Surgery Pre-op & Post-op Course
Pre-op Course
All procedures require medical clearance by an internist at HSS which must be done within 28 days prior to your surgery date. We’ll arrange both these appointments and an educational class.
We recommend stopping the use of all anti-inflammatory, fish oil supplements, and other blood-thinning medications one week prior to surgery. Your clearance physician will provide suggestions for additional prescription medications.
Post-op course
Your hospital stay will typically last 1-2 days. Following your joint replacement surgery in Chennai, you’ll be discharged once therapy clears you. You’ll receive visiting nurse and home physical therapy services. Subsequently, outpatient physical therapy will be scheduled. Your first follow-up will occur six weeks after surgery.
On average, return-to-work recovery takes about six to eight weeks, varying based on individual progress. Most patients can resume most sports activities approximately twelve weeks post-surgery.
Understanding Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Total Hip Replacement Surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, involves the replacement of a damaged or deteriorated hip joint with an artificial one. This prosthetic joint is typically made of metal, ceramic, or high-grade plastic, carefully designed to mimic the natural movement and function of the hip. The surgery aims to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or hip fractures.
Types of Total Hip Replacement Surgery
There are several types of total hip replacement surgeries, including:
- Traditional Total Hip Replacement (THR): Involves a large incision for joint access.
- Minimally Invasive THR: Uses smaller incisions, potentially reducing recovery time.
- Anterior Approach THR: Accesses the hip joint from the front, avoiding muscle damage.
- Posterior Approach THR: Involves accessing the joint from the back, preserving the hip’s posterior capsule.
- Hip Resurfacing: Preserves more bone by capping the femoral head rather than replacing it.
Conclusion
Joint replacement surgery is a highly effective and safe procedure that can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic joint pain and stiffness. With advancements in technology and surgical techniques, joint replacement surgeries are becoming more precise, less invasive, and offer faster recovery times.
While there are risks associated with any surgical procedure, the benefits of joint replacement surgery often outweigh the potential risks. It is essential to consult with a qualified orthopaedic surgeon to determine if joint replacement surgery is the right option for you. With proper care and rehabilitation, joint replacement surgery can help restore mobility and allow individuals to return to their daily activities with minimal pain and discomfort.
Additional information to help you prepare for Smart Knee Replacement.