Arthritis causes inflammation and pain in the joints. It is a very common condition, affecting about 50 million people in the United States alone. if you are thinking can you remove arthritis, you should also be aware of the Numerous forms of arthritis that exist, yet the prevalent variant is osteoarthritis. This type arises due to the deterioration of joint cartilage.
Knee arthritis is a common type of osteoarthritis. It can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee. In some cases, it can also lead to difficulty walking and other activities.
Treatments For Can You Remove Arthritis
There is no cure for arthritis, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms and help you get clarity for can surgery remove arthritis. These treatments include:
- Medications: There are many different types of medications that can be used to treat arthritis. Some of these medications are pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Others are anti-inflammatory drugs, such as methotrexate or prednisone.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help to improve the range of motion and strength in the knee. It aids you in reducing pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat knee arthritis. There are many different types of knee surgery, but the most common type is knee replacement surgery.
So, can you remove arthritis from your knee? The answer is, unfortunately, no. There is no cure for arthritis. However, there are treatments that can aid in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life.
If you are experiencing pain or other symptoms of knee arthritis, it is important to see a doctor. They can help you to determine the best course of treatment for your individual situation.
Check out Best Osteoporosis Doctors in India.
Can You Prevent Arthritis?
There is no sure way to prevent arthritis when there arises the question can you remove arthritis from your knee? but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight. Excess weight puts extra stress on your joints which can increase the risk of developing arthritis.
2. Exercise Regularly. Exercise helps to strengthen your muscles and joints, which can help to protect them from damage.
3. Eat a Healthy Diet. A healthy diet includes vegetables, fruits, and whole grains. This reduces inflammation and protects your joints from damage.
4. Avoid Smoking. Smoking can damage your joints and increase your risk of developing arthritis.
If you have any concerns regarding the risks of developing arthritis, talk to your arthritis doctor. They can help you to develop a plan to reduce your risk and manage any symptoms that you may develop.
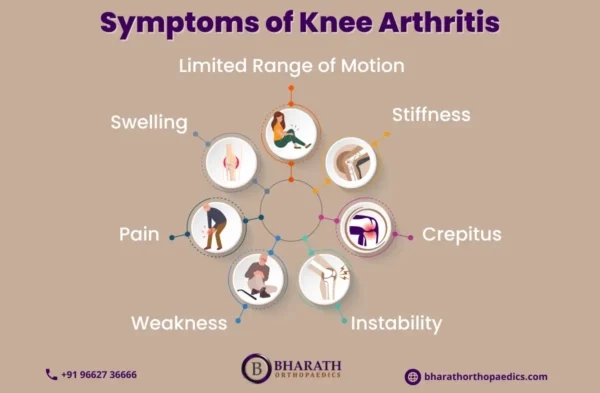
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis is a degenerative condition that causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee joint. The most common type is osteoarthritis, which occurs due to cartilage wear and tear, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that affects multiple joints.
Key symptoms of knee arthritis include:
- Pain – Persistent or worsening pain, especially after activity or prolonged sitting.
- Stiffness – Difficulty bending or straightening the knee, often worse in the morning.
- Swelling – Inflammation due to excess fluid buildup in the joint.
- Cracking or Popping Sounds – Grinding, clicking, or popping noises when moving the knee.
- Weakness and Instability – The knee may feel weak or give out during movement.
- Reduced Range of Motion – Difficulty performing everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or kneeling.
Symptoms may worsen over time, affecting mobility and quality of life. Early detection and management can help slow progression and alleviate discomfort. If knee pain persists or worsens, seeking medical evaluation is essential to determine the severity and appropriate treatment.
How is Knee Arthritis Diagnosed?
Knee arthritis is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. A healthcare provider evaluates symptoms, lifestyle, and risk factors to determine the severity of the condition.
Diagnosis Process:
- Medical History & Physical Exam – The doctor asks about symptoms, pain patterns, and previous injuries. They check for joint swelling, tenderness, stiffness, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays – Reveal cartilage loss, bone spurs, and joint space narrowing, common in osteoarthritis.
- MRI Scans – Provide detailed images of soft tissues, useful for detecting early cartilage damage and ligament issues.
- Laboratory Tests:
- Blood Tests – Help rule out rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases.
- Joint Fluid Analysis – A sample of synovial fluid is tested for infection, inflammation, or gout.
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent worsening symptoms. Identifying arthritis at an early stage allows for more effective treatment, potentially slowing its progression and improving joint function.
How is Knee Arthritis Treated?
Knee arthritis treatment focuses on reducing pain, improving mobility, and slowing disease progression. Treatment options vary based on severity and individual needs.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Medications: Pain relievers (acetaminophen, NSAIDs), corticosteroid injections, and hyaluronic acid injections help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises improve joint stability and flexibility, reducing discomfort.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight management, low-impact activities (swimming, cycling), and proper footwear can ease joint stress.
- Assistive Devices: Braces, knee sleeves, or walking aids provide extra support.
Surgical Treatments:
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to remove damaged cartilage and debris.
- Osteotomy: Realigns the knee joint to shift weight from the damaged area.
- Knee Replacement (Partial or Total): For severe cases, artificial joint implants restore function.
A personalized treatment plan helps patients manage symptoms effectively, enhancing their quality of life. Early intervention can delay or even prevent the need for surgery.
What are the Complications of Knee Arthritis?
Knee arthritis can lead to various complications if left untreated, significantly affecting mobility and daily activities. The progressive nature of the condition can cause:
Common Complications:
- Chronic Pain and Stiffness: Persistent pain can interfere with daily activities, making walking, standing, or climbing stairs difficult.
- Joint Deformity: Advanced arthritis can cause bone overgrowth (bone spurs) and misalignment of the knee, leading to a bow-legged or knock-knee appearance.
- Reduced Mobility: As arthritis worsens, movement becomes increasingly limited, impacting independence and quality of life.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakened muscles around the knee result from reduced activity, further worsening joint stability.
- Increased Risk of Falls: Knee instability can lead to falls and injuries, especially in older adults.
- Emotional and Mental Impact: Chronic pain and limited mobility may lead to anxiety, depression, and reduced social interactions.
Proper treatment and lifestyle changes can help prevent these complications. Early intervention with medications, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve knee function and overall well-being.If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis and treatment after getting clarity from the question, can you remove arthritis from your knee.If you have knee arthritis, it is important to see your doctor regularly to monitor your condition and make sure that you are getting the best possible treatment.
Can Knee Arthritis Be Prevented?
While knee arthritis cannot always be completely prevented, certain lifestyle choices and preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing the condition or slow its progression. Since arthritis is often linked to aging, genetics, and joint wear and tear, taking proactive steps to protect knee health is crucial.
Preventive Measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of cartilage breakdown. Maintaining a healthy BMI reduces joint strain.
- Stay Active: Regular low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking help strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing better joint support.
- Strengthen Leg Muscles: Strong quadriceps and hamstrings help stabilize the knee joint, reducing strain and minimizing arthritis risk.
- Avoid High-Impact Activities: Excessive running, jumping, or repetitive stress on the knees can accelerate cartilage wear. Opt for joint-friendly activities.
- Protect Joints from Injury: Proper footwear, knee braces, and using correct posture while lifting or exercising help prevent injuries that could lead to arthritis.
- Eat a Joint-Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins C and D, and calcium, supports joint health.
By adopting these habits, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing knee arthritis and maintain mobility and knee function for longer.
Conclusion
To conclude, if you have any concerns about your risk of developing knee arthritis, or if you have a query can you remove arthritis from your knee, then you can talk to Dr. Bharath from Bharath Orthopaedics as this expert can help you to develop a personalized treatment plan to reduce your risk.
Read also: Limb Lengthening Surgery
